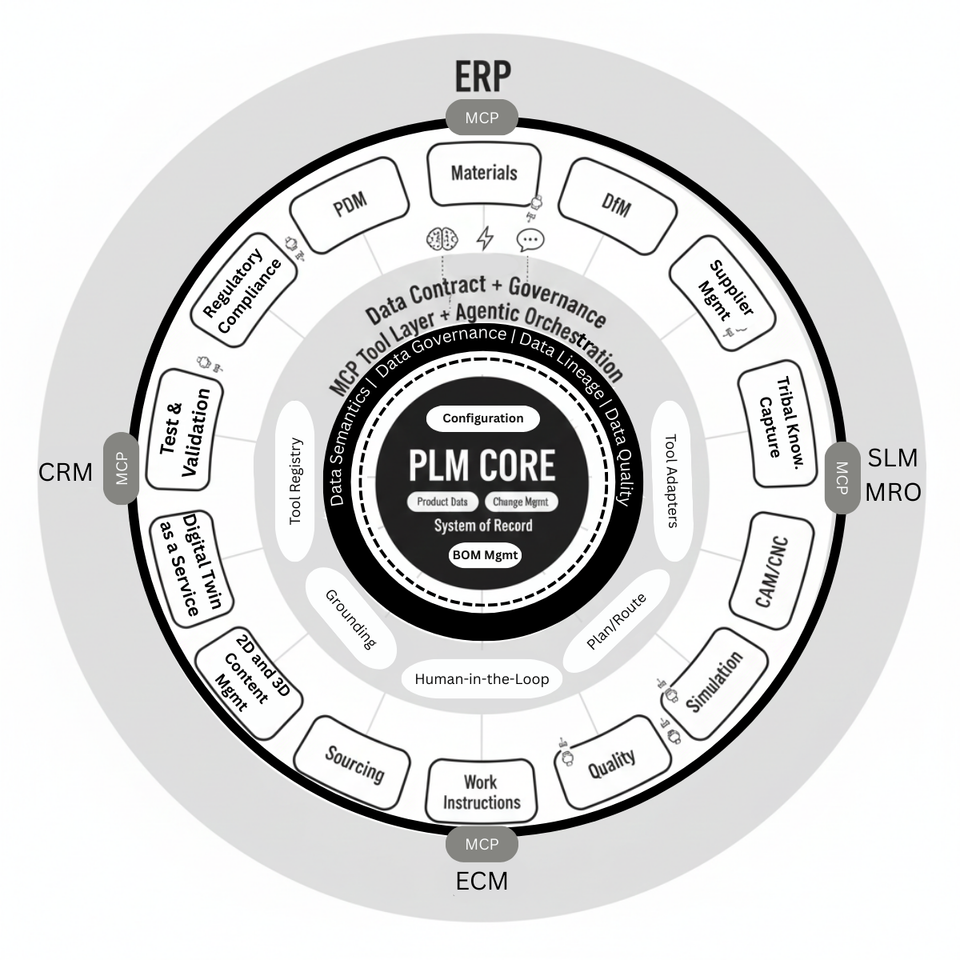
Thread-Centric PLM Architecture Scorecard (12 criteria)
Scoring (0–3)
- 0 = Missing (not present / not used)
- 1 = Ad hoc (manual, inconsistent, tribal)
- 2 = Implemented (works in places, gaps exist)
- 3 = Standardized + monitored (policy-driven, tested, observable)
Use one “Evidence” line per item (what you’d show to prove the score).
A) Truth + Governance (Data Contract)
1) System-of-Record clarity
Is there a clear authority per object/state (part, BOM, change, config, effectivity, requirement, as-maintained)?
Evidence: RACI / SoR map, published data ownership rules.
2) Canonical IDs + versioning
Stable identifiers, revision rules, baselines, effectivity, variant/config control across tools.
Evidence: ID policy, revision/effectivity model, baseline reports.
3) Data semantics (shared meaning)
Common ontology + relationship constraints (not just fields): what objects mean and how they connect.
Evidence: ontology/knowledge model, schema contracts, mapping docs.
4) Lineage + provenance
Can you prove where data came from, what transformed it, who approved it, and when?
Evidence: audit logs, provenance metadata, trace reports.
B) Execution + Agentic (MCP Tool Layer)
5) Tool coverage (real verbs)
Key lifecycle actions are exposed as callable tools (create/approve/publish/validate), not read-only APIs.
Evidence: tool registry, API catalog, top workflows mapped to tool calls.
6) Runtime policy enforcement
Access rules applied consistently at execution time across tools (entitlements, least privilege, segregation of duties).
Evidence: policy engine rules, authZ logs, role tests.
7) Human-in-the-loop + exception handling
Approvals, escalation, exception queues, rollback paths for automated actions.
Evidence: approval workflow, exception dashboard, rollback procedure.
8) Grounding + citations for actions
Every agent/tool action is tied to governed records with citations (what data + which versions were used).
Evidence: action logs with record references, citation trails, replayability.
C) Composability + Enterprise Reach
9) Swap-ability of edge capabilities
Can you replace a capability app (materials, work instructions, etc.) without replatforming the core?
Evidence: decoupled interfaces, contract adherence tests, replacement playbook.
10) Event-driven lifecycle flow
Changes propagate via events (pub/sub) with near-real-time updates vs batch sync and spreadsheets.
Evidence: event bus topics, SLAs/latency metrics, consumers list.
11) Enterprise tool gateway (ERP/CRM/SLM/ECM)
Outer systems are reached via standardized tools/adapters, not bespoke point integrations.
Evidence: tool adapters per system, integration tests, change publish workflow.
12) Operational quality (SLOs + observability)
Monitoring, SLOs, error budgets, integration tests, and auditability exist for the thread end-to-end.
Evidence: dashboards, alerts, SLO definitions, test suites, incident postmortems.
Interpretation bands (quick)
- 0–12: Suite-bound (high integration/upgrade/AI taxes)
- 13–24: Transitional (mixed model, inconsistent controls)
- 25–36: Thread-centric (governed, execution-ready, composable)
